Medication
Dosage Form
They are the means by which drug molecule are delivered to sites of action within the body. They have two major portions:
- API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients)
- Excepients (non-drug-parts)
Classification of Dosage Form
Routes of Administration
A route of
Administration is the path by which a drug, fluid, poison or other substance is
taken into the body.
Parenteral
Classification
Tablets
Tablets
may be defined as solid pharmaceutical dosage forms containing drug substances
with or without suitable diluents and prepared either by compression or molding
methods.
Types of Tablets
Orally Ingested
- Compressed tablet, e.g. Paracetamol
tablet
- Multiple compressed tablet
- Delayed release tablet, e.g. Enteric
coated Bisacodyl tablet
- Sugar coated tablet, e.g.
Multivitamin tablet
- Film coated tablet, e.g. Metonidazole
tablets and Chewable Tablets such as Antacids.
Tablets used in oral cavity
- · Buccal tablet, eg. Vitamin-c tablet
- ·
Sublingual tablet, eg. Vicks
Menthol tablet
- ·
Troches or lozenges
- ·
Dental cone
Tablets administered by other routes
- Implantaton Tablets
- Vaginal Tablets eg: Clotrimazole tablet
Tablets used to prepare solutions
- · Effervescent tablet, e.g. Dispirin
tablet (Aspirin)
- · Dispensing tablet, e.g. Enzyme tablet
(Digiplex)
- · Hypodermic tablet
- · Tablet triturates e.g. Enzyme tablet (Digiplex)
Capsules
They
are solid dosage forms in which medicinal agents and inert substances are
enclosed in a small shell of gelatin. Capsules are mainly of two types:
- Hard Gelatin Capsule
- Soft gelatin Capsule
SYRUPS
Concentrated
aqueous preparations of 85% of sugar or sugar substitute with or without
flavouring agents and medicinal substances.
- 1. Medicated Syrups
- 2. Non-
Medicated Syrups
Oitment, Cream, Paste, Gel
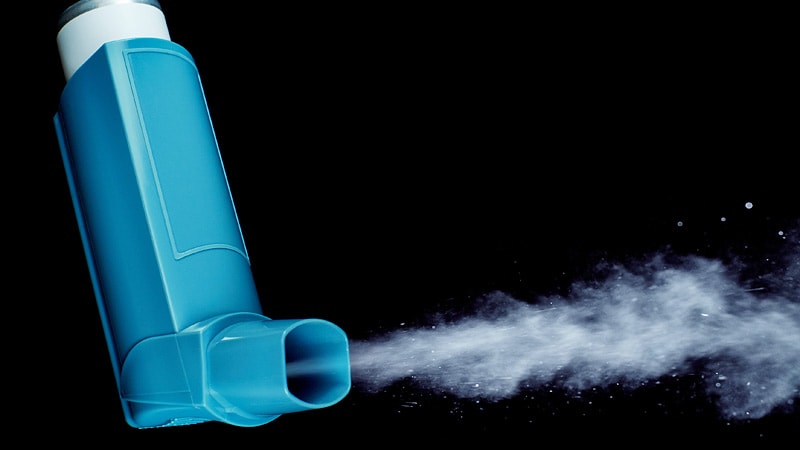
Aerosols and Inhaler
Aerosol
is a pressurized dosage forms containing one or more therapeutic active
ingredients which upon actuation emit a fine dispersion of liquid and/or solid materials
in gaseous medium.







Comments
Post a Comment